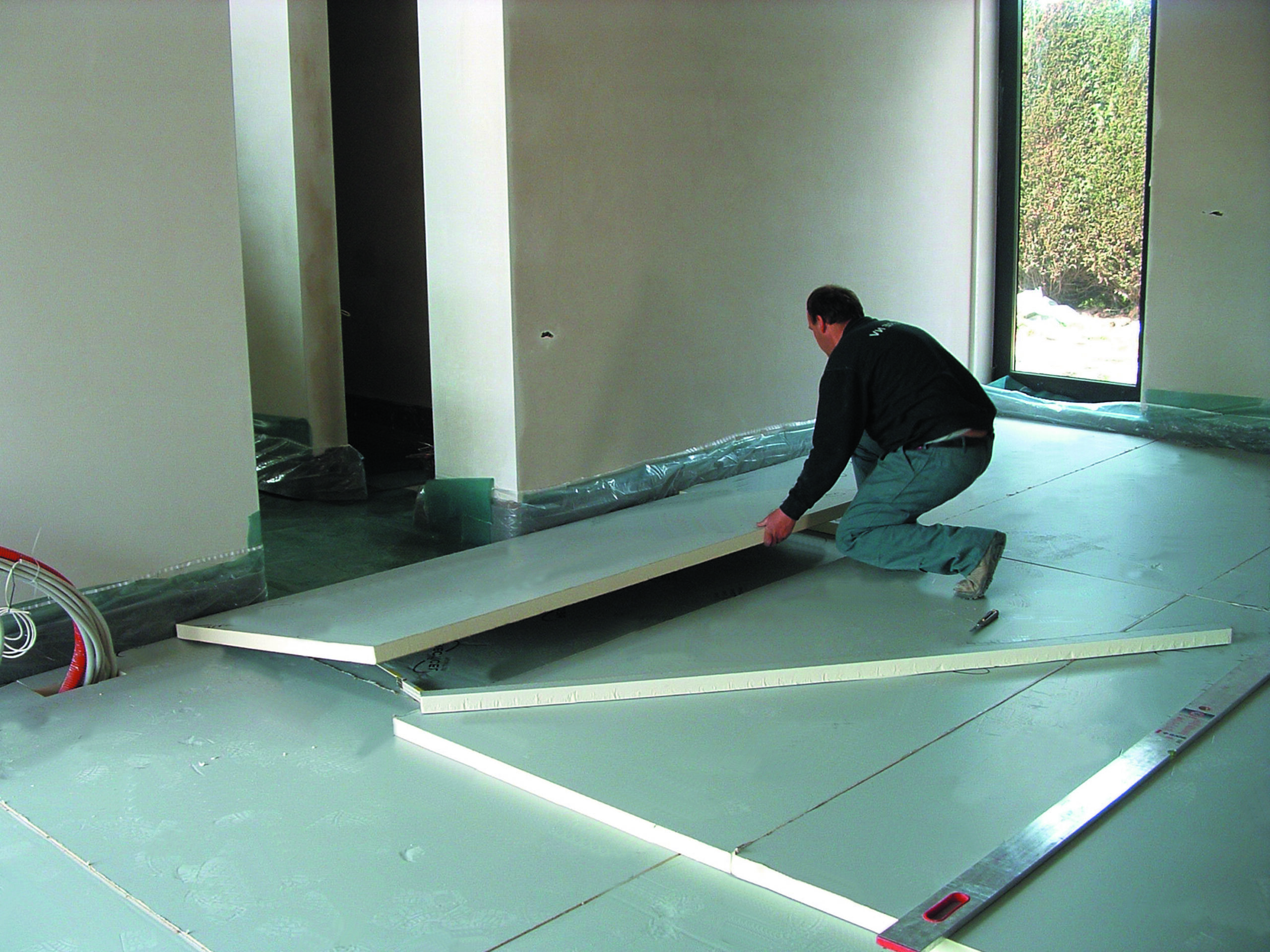
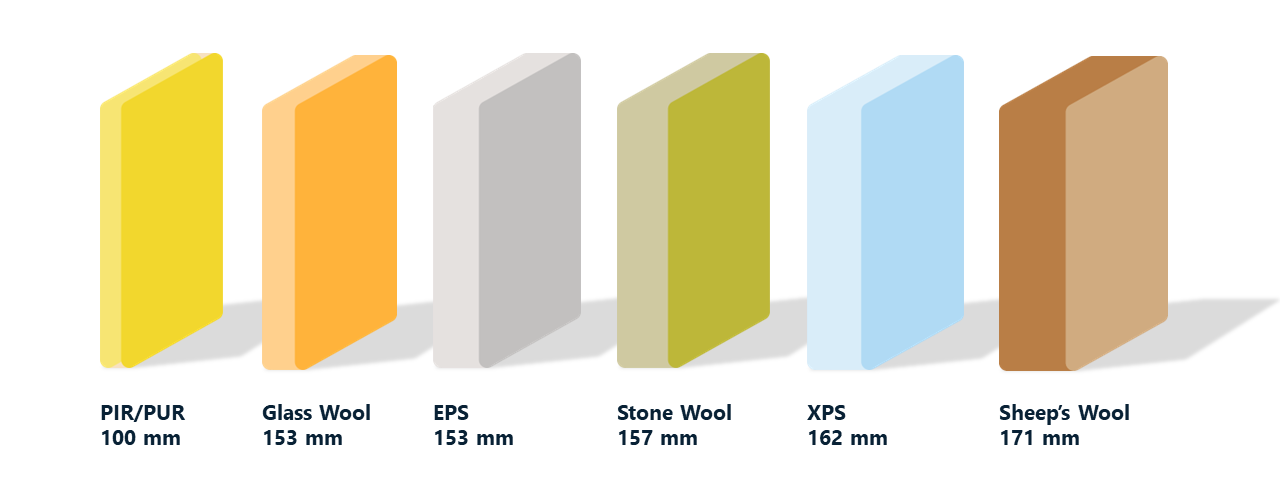
Boards are typically used in masonry cavity walls, timber or steel frame walls, pitched and flat roof applications, warm roofs and all floor types. They can also be used with plasterboard laminates and in composite panels or sandwich panels with metal facings.
PIR and PUR both have excellent thermal insulation values and are highly space efficient, durable and lightweight. PIR, with its high compressive strength and cost-efficient assembly offers a competitive payback period when compared with other insulation types.